
Inflammation is a local and protective response to a cellular injury arising from a lesion, an infection, or an illness. It is a key mechanism of innate immunity, the first line of defense of an organism in contrast to adaptive immunity, which is a specific, albeit slower, line of defense recognizing and keeping memory of already met pathogens or foreign materials.
In exceptional cases abnormal immune response to a body part may produce immune effectors attacking self-component of the body, creating a chronic auto-inflammation that could generate an autoimmune disease where a specific tissue is repeatedly injured by its own mechanism of defense.
Some of these auto-immune diseases are characterized by a pivotal role of type1 interferon and most of them involve the generation of harmful antibodies.
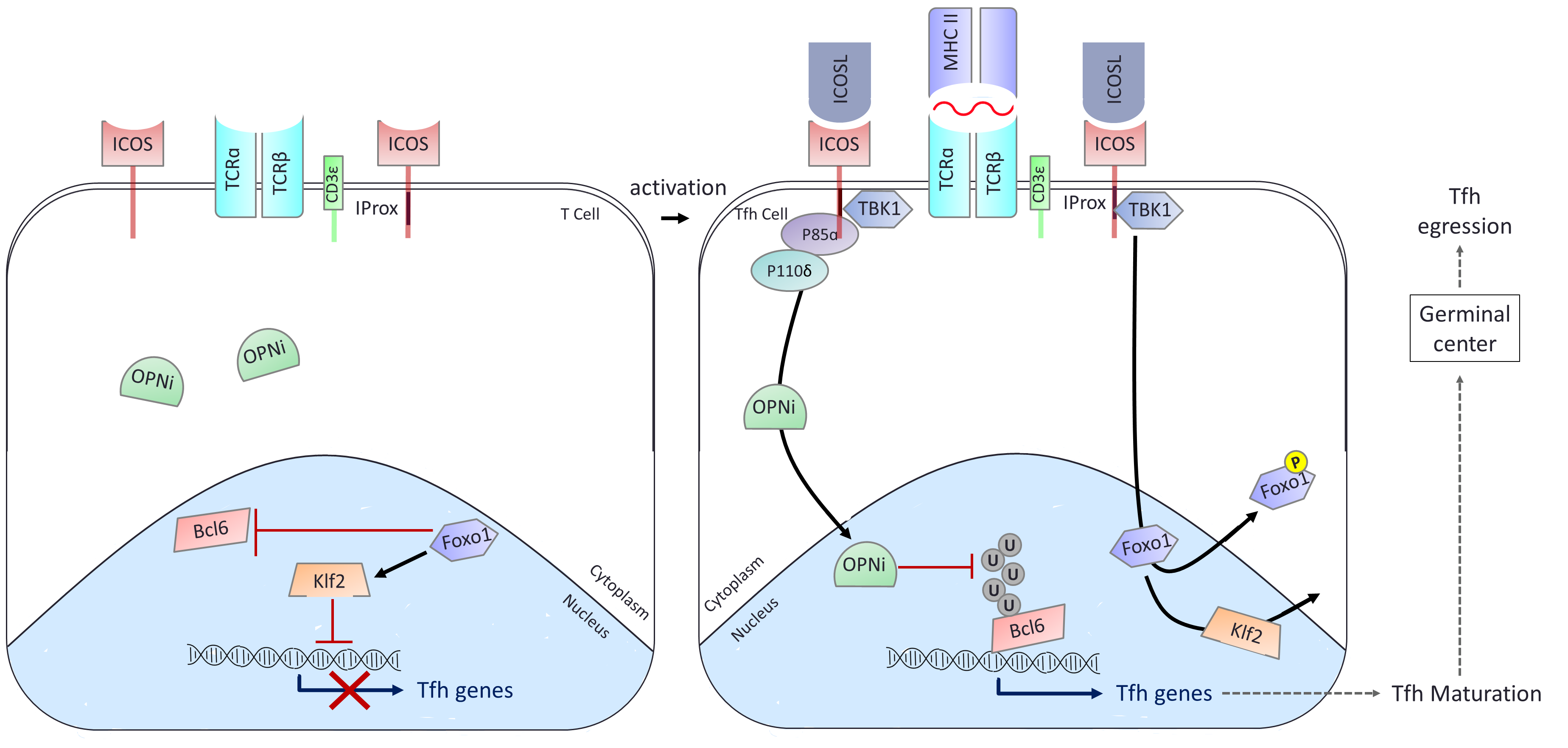
On one side, TBK1 has been shown to be a key component of the intracellular cascade of the ICOS receptor being required for full maturation of the T follicular helper (Tfh) cell after ICOSL stimulation. By blocking TBK1 it is therefore possible to refrain Tfh maturation within germinal centers and hence minimize humoral response e.g. the deleterious production of auto-antibodies in autoimmune diseases.
On another side, inhibition of IKKε/TBK1 activities also directly block production of type-1 interferon triggered by several innate immune pattern recognition receptors involved in auto-immunity such as STING or TLR3. Type-1 interferon is a key cytokine of the innate immunity system required to trigger production of Interferon-stimulated gene (ISGs) such as BAFF, a key target protein for treatment of lupus or other significant rheumatic or autoimmune conditions known to be associated with increased B-cell proliferation and activity.
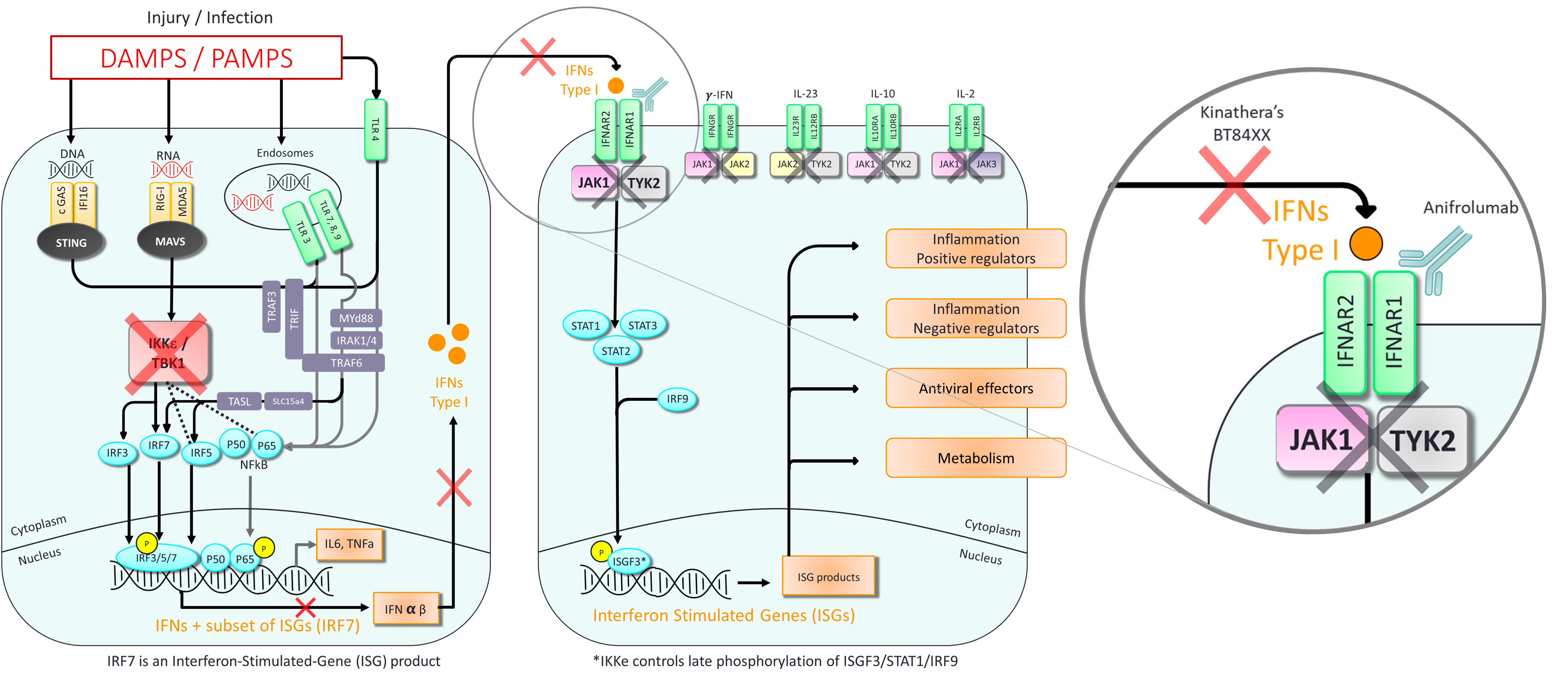
Our goal is to advance new and safe first-in-class therapeutics for the treatment of acute GvHD and interferon-linked immune diseases, especially in orphan and rare autoimmune indications. Our new chemistry enables specific binding to its target, superior kinase selectivity compared to previous inhibitor of the target and fresh Intellectual Property.

Convenient oral daily dosing confers indeed enhanced safety by offering temporary treatment shutdown whether a patient infection would require it. This is in contrast with other treatment regimen of infused antibodies where product will remain blocking the type 1 interferon pathway for several weeks once injected and which solely modulates type 1 interferon receptor. The targeted activity of kinatheras’s compounds also differentiates them from other oral JAK1/TYK2 or IRAK1/4 inhibitors that block signaling of type 1 interferon and multiple other cytokine or TLR receptors including anti-inflammatory cytokines bearing potential for side toxicity and black-box warning.